From Optflux
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
[[Image:IntegratedSimulationOperaion.png]] | [[Image:IntegratedSimulationOperaion.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ClipboarIntegratedSi_mulation.png]] | ||
==Critical Genes== | ==Critical Genes== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 51: | ||
===How to do load critical genes from a file=== | ===How to do load critical genes from a file=== | ||
[[Image:PathForCriticalGenes.png]] | [[Image:PathForCriticalGenes.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:LoadCriticalRegulatoryGenesOperation.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ClipboardAfterCriticalGenes.png]] | ||
===How to determining essential genes=== | ===How to determining essential genes=== | ||
[[Image:PathForCriticalGenes.png]] | [[Image:PathForCriticalGenes.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ComputeCriticalGenesOperation.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ClipboardAfterCriticalGenes.png]] | ||
| + | |||
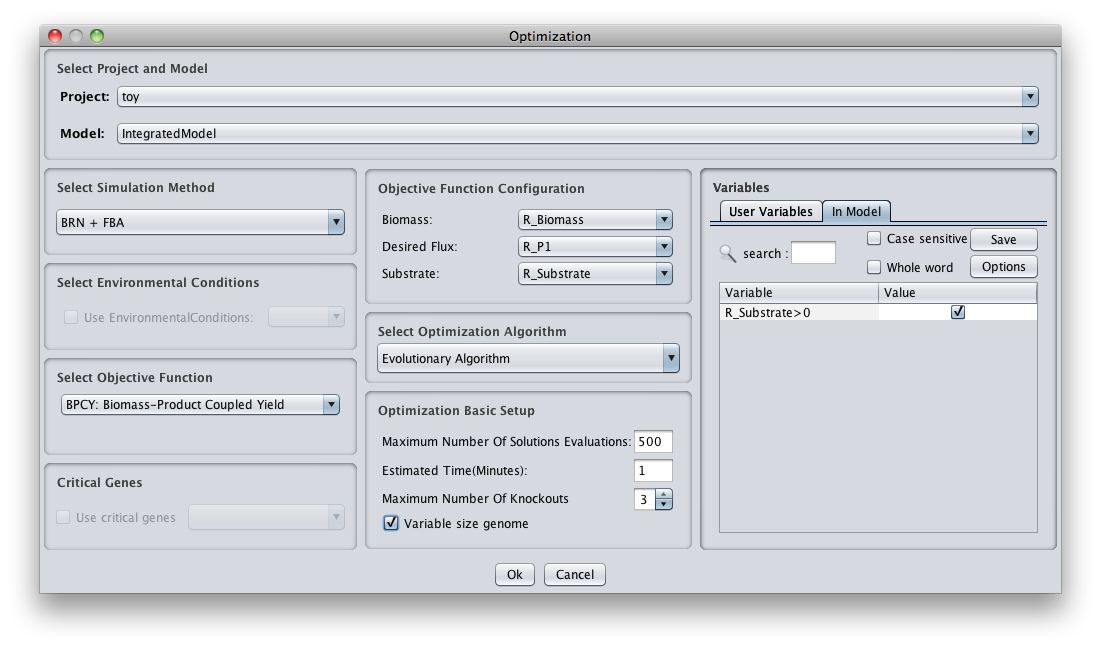
==How to optimise the gene knockouts set== | ==How to optimise the gene knockouts set== | ||
[[Image:PathForSimAndOpt.png]] | [[Image:PathForSimAndOpt.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:IntegrateOptimizationOperation.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:ClipboardAfterIntegrateOptimization.png]] | ||
Revision as of 17:48, 8 July 2010
Contents
Example file
You can download it here ->
This tutorial uses this example based on an example from J. Kim and J. Reed.OptORF: Optimal metabolic and regulatory perturbations for metabolic engineering of microbial strains. BMC, 2010
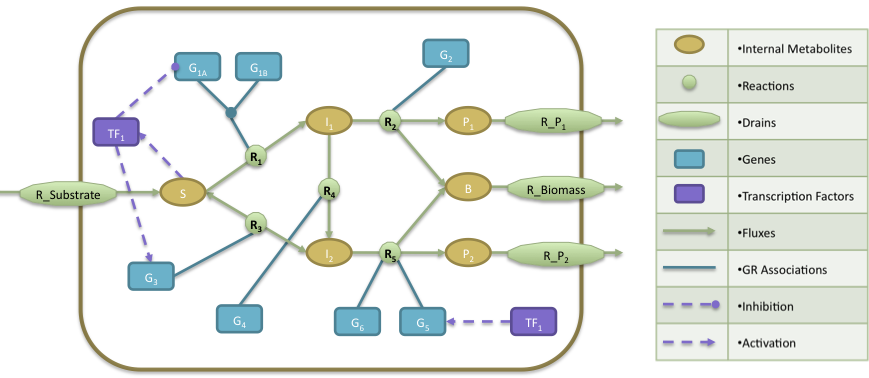
- The regulatory model is composed by a transcription factor (TF1) that is activated when metabolite S is present, activates the expression of two genes (G3, G5) and represses the expression of gene G1A.
- The Gene Reactions rules said us that: R1 is catalyzed when the gene G1A and G1B are activated; R2 is catalyzed by the gene G2; R3 and R4 are catalyzed by the genes G3 and G4, respectively; finally, R5 can be catalyzed by either genes G5 or G6.
- In the metabolic level, the substrate (S) is utilized to produce biomass (B) and by-products P1 and P2. The cellular objective is to maximize biomass production (B) and the engineering objective is the production of P1. Reaction R2 converts the internal metabolite I1 into product P1 and 0.08 biomass (B), whereas reaction R5 converts the internal metabolite I2 into product P2 and 0.12 Biomass. The stoichiometric coefficients of all other reactions reflect a one-to-one relationship between molecule quantities.
Brief tutorial
This brief tutorial will help you to begin working with RegulatoryTool4OptFlux.
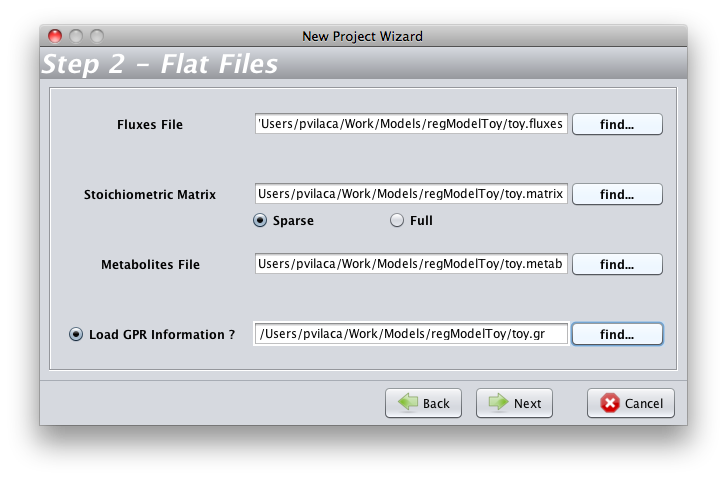
- To start, you will need load a model in OptFlux(see how to here). In the New Project Wizard you have to chose the the toy.fluxes file as the Fluxes File; the toy.matrix file as the Stoichiometric Matrix; the toy.metab file as the Metabolites File and the toy.gr file as the Load GPR Information.
- On the wizard Step3, you have to chose indexing started at zero(0)
- You must pay attention to select a correct biomass flux (R_Biomass).
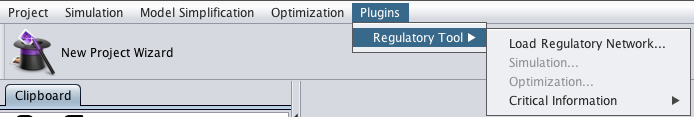
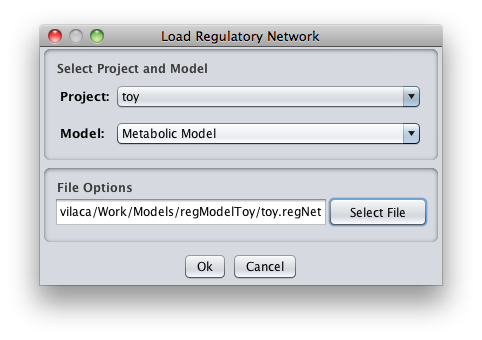
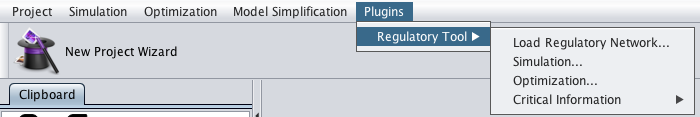
How to integrate a regulatory model
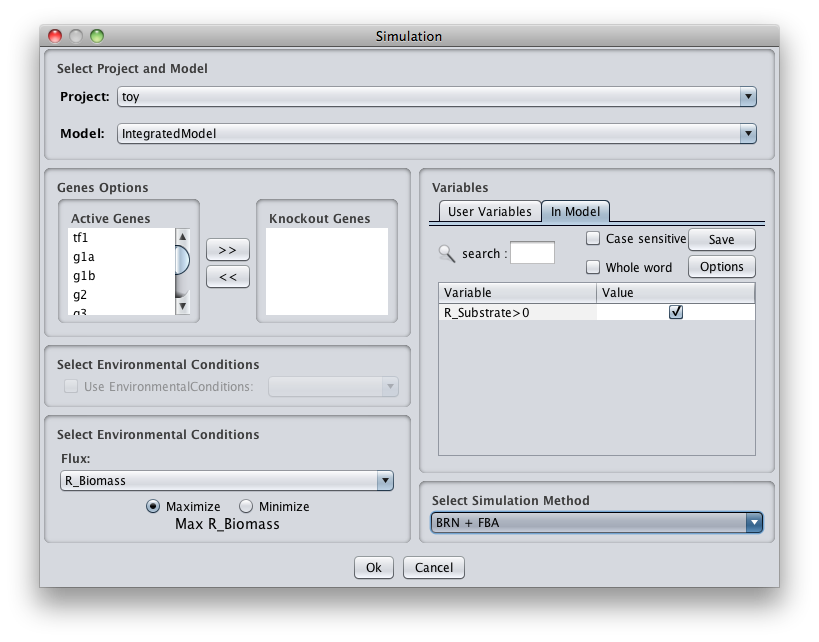
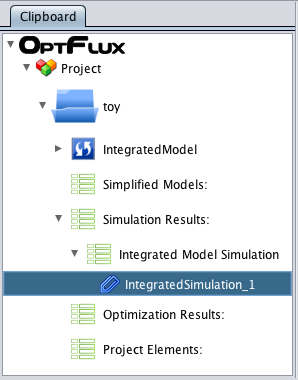
How to do a mutant simulation
Critical Genes
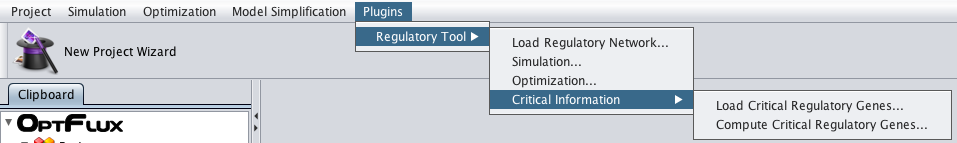
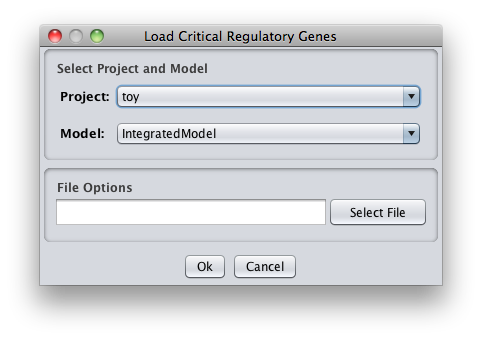
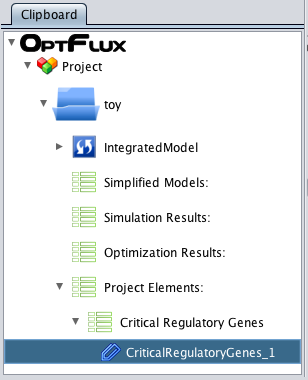
How to do load critical genes from a file
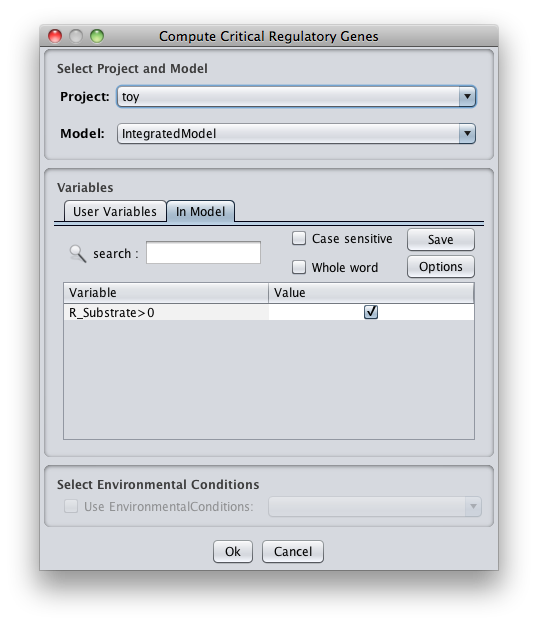
How to determining essential genes