(→Framework description) |
(→Framework description) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* Phenotype methods: | * Phenotype methods: | ||
| − | ** FBA, pFBA, ROOM, MOMA, | + | ** FBA, pFBA, ROOM, MOMA, Linear MOMA, MiMBL |
* Optimization methods: | * Optimization methods: | ||
** EA, SA, SPEA2 | ** EA, SA, SPEA2 | ||
Revision as of 02:51, 8 February 2013
Contents
Framework description
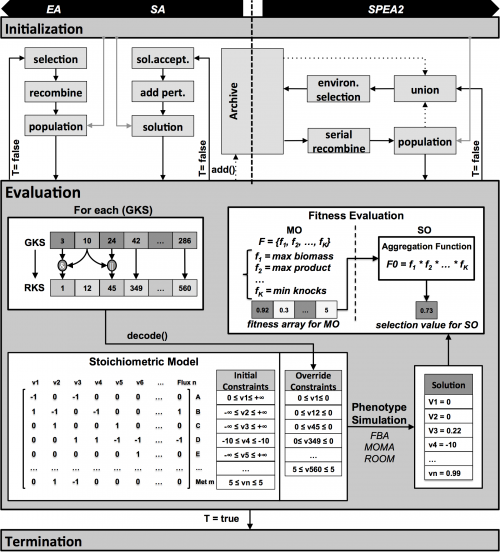
The new version of OptFlux's Strain Optimization plug-in includes all the previous single objective (SO) optimization methods, seamlessly integrated with the new multi-objective (MO) architecture.
In this version of the Optimization plug-in, the following features are available:
- Phenotype methods:
- FBA, pFBA, ROOM, MOMA, Linear MOMA, MiMBL
- Optimization methods:
- EA, SA, SPEA2
- Single and multi-objective
- Types of Knockout:
- Reactions, Genes
- Over/under expression optimization
The Archive Manager
In this version of OptFlux, some changes were applied to the EA and SA algorithms, regarding the information that is kept during each run, although not changing their functioning nor the best final solution. The major change was the implementation of an archive that keeps the best solutions found by the EA and SA during the run. This is not used by the algorithms for selection or for creating new solutions, but allows having a richer final result. The archive runs in a parallel thread, and smartly manages the solutions that are kept, removing duplicate solutions and non-better super solutions of already existing ones.
Solution Simplification
The end step of an optimization procedure is the solution simplification. These heuristics although intelligent, may generate solutions that include unnecessary knockouts/regulations. To prevent this, only the optimal genetic modifications are kept.
Methods
Single Objective Algorithms
=